What is a PET Test for Cancer?
A PET scan (positron emission tomography) is a type of imaging test that uses a radioactive tracer to detect cancer and other diseases. The tracer is injected into the body and then absorbed by cells. The cells that are most active, such as cancer cells, absorb the most tracer. A scanner is then used to detect the tracer and create images of the body.
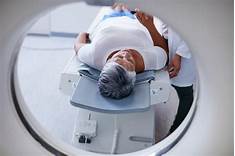
How Does a PET Scan Work?
1. A small amount of a radioactive tracer is injected into a vein in your arm.
2. The tracer travels through your bloodstream and is absorbed by cells throughout your body.
3. Cancer cells and other cells that are rapidly dividing absorb more tracer than normal cells.
5. A scanner detects the tracer and creates images of your body.
6. The images are then interpreted by a doctor to look for signs of cancer or other diseases.
What Are the Benefits of a PET Scan?
1. PET scans can help doctors diagnose cancer at an early stage, when it is more likely to be curable.
2. PET scans can help doctors determine the extent of cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body.
3. PET scans can help doctors monitor the response of cancer to treatment.
4. PET scans can help doctors detect recurrence of cancer after treatment.
What Are the Risks of a PET Scan?
1. The amount of radiation used in a PET scan is low, but it can still increase your risk of developing cancer.
2. The radioactive tracer can cause allergic reactions in some people.
3. PET scans can be expensive.
Who Should Get a PET Scan?
PET scans are typically used to diagnose and monitor cancer. They may also be used to diagnose and monitor other diseases, such as heart disease, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease.
Declaration: All article resources on this website, unless otherwise specified or labeled, are collected from online resources. If the content on this website infringes on the legitimate rights and interests of the original author, you can contact this website to delete it.




